
A shift in market dynamics calls for an alternative approach
Now that inflation is back in the global economy, investors are facing a radically different landscape from the one experienced since the 2008 financial crisis. Over the past two years, yields across fixed income segments have experienced multiple-fold increases. Core government bond yields are now out of negative territory, those on emerging market bonds have risen by a factor of two (from 4.5% to nearly 9%), and those on European high yield indices have gone from 2.3% to more than 7% – a threefold increase. The negative correlation between bonds and equities, that diversified portfolios enjoyed for nearly 20 years, has come to an end.
And since the inflationary pressure will likely continue for at least the medium term, investors will have to find new ways of diversifying their portfolios.
Merger arbitrage strategy to diversify your potfolio
Merger arbitrage is an alternative strategy whose objective is to take advantage of price discrepancies, observed after the announcement of an M&A (Merger & Acquisition) transaction on a listed company. It is especially suited for current market environment, as it presents an effective hedge in rising rate or inflationary environment. The strategy often displays a lower volatility compared to stocks with low correlation with traditional asset classes such as equities and bonds.
Merger arbitrage strategies typically involve building a diversified portfolio containing 50–60 holdings, each in a company involved in an M&A deal. The main risk associated with this portfolio is idiosyncratic – the market risk has been replaced by deal-failure risk. In other words, whereas stock-price movements generally track the broader market, movements in merger arbitrage spreads follow their own dynamic that’s driven by the steps in the corresponding deal. That means merger arbitrage strategies are only weakly correlated with equity markets – and with bond markets, too.
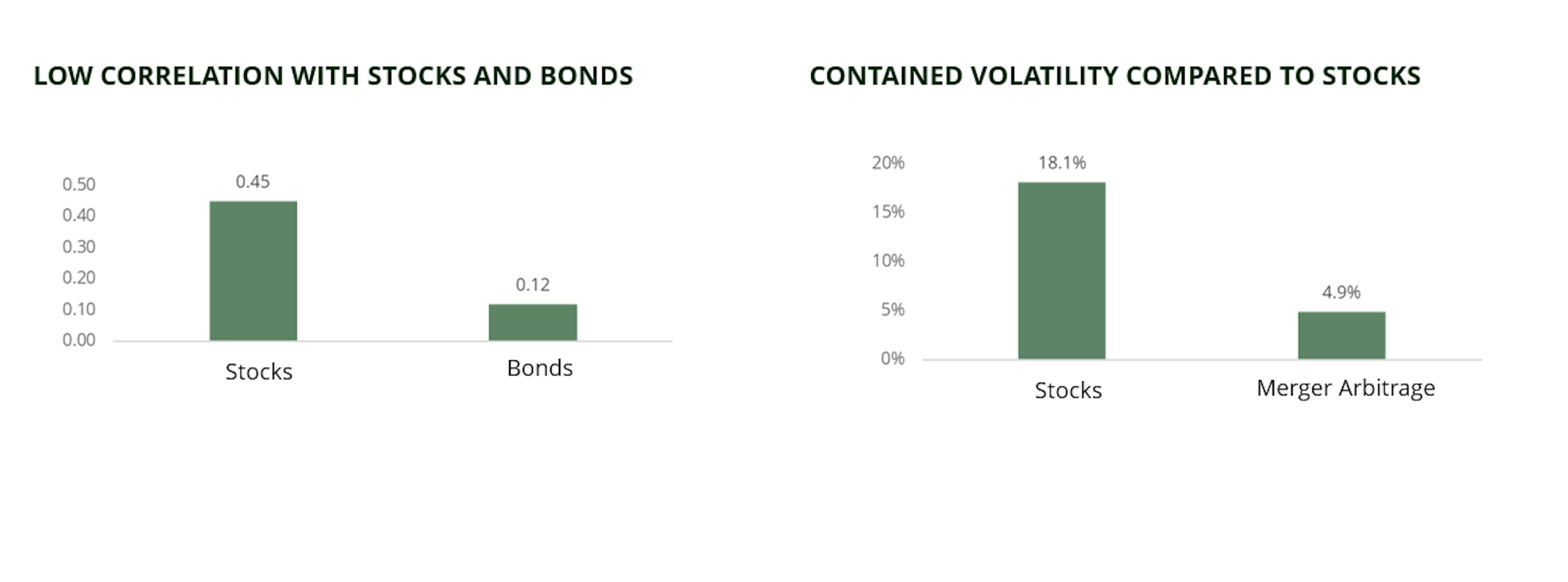
For illustrative purpose only. The HFRI Merger Arbitrage Index is used as a proxy for the merger arbitrage universe. Sources: Carmignac, Bloomberg at 30/06/2023.
Natural protection against high interest rates
Merger arbitrage strategies are particularly well-suited to times of rising interest rates. Since the risk-free rate is one of the two components of a merger arbitrage spread, increases in this rate – i.e., the short-term interest rate – will automatically push up the expected return on a merger arbitrage strategy for the same level of risk.
This pattern appears to hold over extended periods of time. For instance, merger arbitrage spreads followed movements in interest rates between 1990 and 2008: they declined after the dot-com bubble burst in 2001 and rose during the 2004–2007 economic recovery. But the correlation was undone by the 2008 financial crisis and the ensuing era of 0% interest rates engineered by central banks.
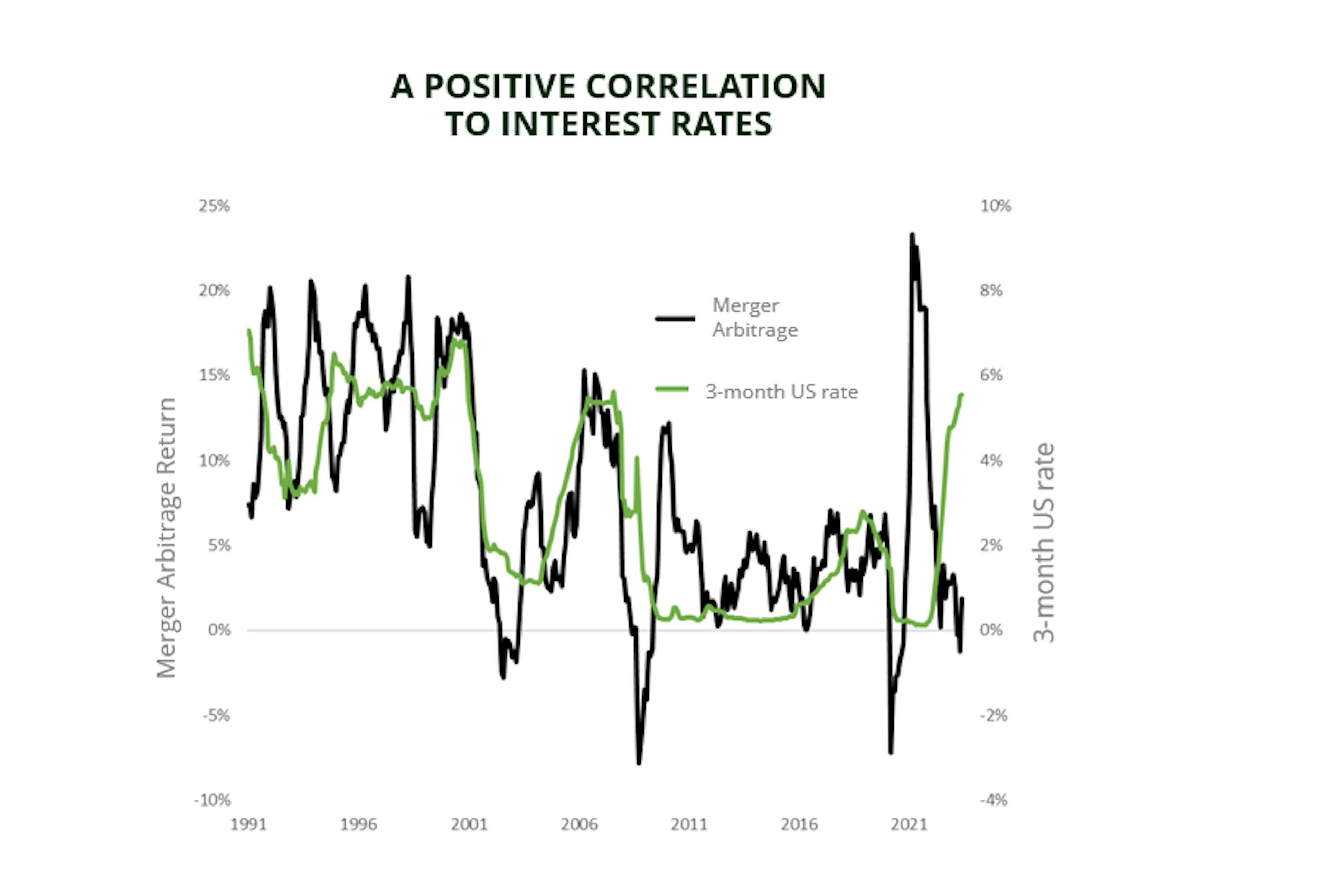
For illustrative purpose only. We use the HFRI Merger Arbitrage Index to describe the Merger Arbitrage universe. Source: Carmignac, Bloomberg. Data as of 30/06/2023.
Merger arbitrage at Carmignac
At Carmignac, we’ve been expanding our alternative-investment capabilities for years and currently manage nearly €2 billion in this asset class. We formed a merger arbitrage team and appointed Fabienne Cretin-Fumeron and Stéphane Dieudonné as Fund managers. This move came in response to growing demand from investors seeking to diversify away from conventional asset classes and into those with reduced volatility and uncorrelated returns.
We launched two merger arbitrage Funds: Carmignac Portfolio Merger Arbitrage, which has a defensive profile and 2%–4% expected volatility; and Carmignac Portfolio Merger Arbitrage Plus, which is more dynamic and has 5%–7% expected volatility. These funds aim to seize M&A opportunities in the main developed countries. They’re both classified as Article 8 under the SFDR and are open to professional and retail investors in several European countries.
Carmignac Portfolio Merger Arbitrage A EUR Acc
- Recommended minimum investment horizon
- 3 years
- Risk indicator*
- 2/7
- SFDR - Fund Classification**
- Article 8
*Risk Scale from the KID (Key Information Document). Risk 1 does not mean a risk-free investment. This indicator may change over time. **The Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) 2019/2088 is a European regulation that requires asset managers to classify their funds as either 'Article 8' funds, which promote environmental and social characteristics, 'Article 9' funds, which make sustainable investments with measurable objectives, or 'Article 6' funds, which do not necessarily have a sustainability objective. For more information please refer to https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2019/2088/oj.
Main risks of the fund
Carmignac Portfolio Merger Arbitrage Plus A EUR Acc
- Recommended minimum investment horizon
- 5 years
- Risk indicator*
- 2/7
- SFDR - Fund Classification**
- Article 8
*Risk Scale from the KID (Key Information Document). Risk 1 does not mean a risk-free investment. This indicator may change over time. **The Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) 2019/2088 is a European regulation that requires asset managers to classify their funds as either 'Article 8' funds, which promote environmental and social characteristics, 'Article 9' funds, which make sustainable investments with measurable objectives, or 'Article 6' funds, which do not necessarily have a sustainability objective. For more information please refer to https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2019/2088/oj.
Main risks of the fund
Related articles

Carmignac Merger Arbitrage: Letter from the Portfolio Managers
![[Main Media] [Funds Focus] Bridge](https://carmignac.imgix.net/uploads/article/0001/02/26ad7f7eb70cc9f1137127c5b230d8042189f9e1.jpeg?auto=format%2Ccompress&fit=fill&w=3840)
Carmignac Absolute Return Europe: Letter from the Fund Managers

Carmignac Portfolio Long Short European Equities: Letter from the Fund Manager
MARKETING COMMUNICATION. Please refer to the KID/prospectus of the fund before making any final investment decisions.
Source: Carmignac, 13/11/2023. This document may not be reproduced, in whole or in part, without prior authorisation from the management company. It does not constitute a subscription offer, nor does it constitute investment advice. Reference to certain securities and financial instruments is for illustrative purposes to highlight stocks that are or have been included in the portfolios of funds in the Carmignac range. This is not intended to promote direct investment in those instruments, nor does it constitute investment advice. The Management Company is not subject to prohibition on trading in these instruments prior to issuing any communication. The portfolios of Carmignac funds may change without prior notice. The information contained in this document may be partial information and may be modified without prior notice. The Management Company can cease promotion in your country anytime. Investors have access to a summary of their rights in English on the following link (paragraph 6): https://www.carmignac.com/en_US/article-page/regulatory-information-1788. The decision to invest in the promoted funds should take into account all their characteristics or objectives as described in their prospectus. Carmignac Portfolio refers to the sub-funds of Carmignac Portfolio SICAV, an investment company under Luxembourg law, conforming to the UCITS Directive. Access to the Funds may be subject to restrictions with regard to certain persons or countries. The Funds may not be offered or sold, directly or indirectly, for the benefit or on behalf of a U.S. person, according to the definition of the US Regulation S and/or FATCA. The Funds present a risk of loss of capital. The risk, fees and ongoing charges are described in the KIDs (Key Information Document). The Funds' respective prospectuses, KIDs, NAV and annual reports are available at www.carmignac.com, or upon request to the Management Company. The KIDs must be made available to the subscriber prior to subscription. The Fund’s respective prospectuses, KIDs and annual reports are available at www.carmignac.ch, or through our representative in Switzerland, CACEIS (Switzerland), S.A., Route de Signy 35, CH-1260 Nyon. The paying agent is CACEIS Bank, Montrouge, succursale de Nyon/Suisse, Route de Signy 35, 1260 Nyon. The KID must be made available to the subscriber prior to subscription.
